Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) and Guideline for Good Warehousing Practices for Raw Material and Packing Materials. The storage of materials in the specified areas according to the classification i.e. poison. Corrosive, Flammable, etc.
Good Warehousing Practices
1.0 Purpose:
-
- The warehousing of Raw materials/packing material is an important aspect for the following reasons:
-
-
- Proper Identification
-
-
-
- The storage of materials in the specified areas according to the classification i.e. poison. Corrosive, Flammable, etc.
-
-
-
- Convenient Traceability
-
-
-
- Issue of Materials.
-
-
-
- Secure Placement of materials
-
-
- The purpose of this SOP is to also define the procedure for partly dispensing of raw and packing materials and to follow FEFO for (Raw Material) and FIFO for (Packing Material) for control and partly dispensing activity
2.0 Scope – Good Warehousing Practices:
-
- This SOP is applicable to Good Warehousing Practices of all raw materials and packaging material.
-
- This procedure is applicable to all partly dispense containers of active, excipients (except solvent) and packing material (Show boxes and Inserts)
3.0 References and Annexures:
-
-
References:
-
-
- In house
-
-
Annexures:
-
-
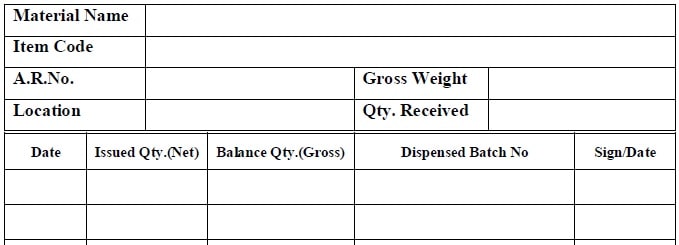
- Annexure1: Format for Loose Label.
4.0 Responsibilities – Good Warehousing Practices:
-
-
Warehouse department shall be responsible for:
-
-
- Follow the procedure of loose dispensed container and box to be dispensed first, affix the loose label for the remaining quantity container after dispensing and investigate in case of any discrepancies during reconciliation.
-
- To improve the proper arrangement of material in the respective area.
-
- To dispose of the material as per the procedure.
-
- Take the necessary precautions to avoid mix-up.
-
- To maintain proper documentation.
-
- Ensure proper implementation of SOP.
-
-
Quality Assurance department shall be responsible for:
-
-
- Check and ensure proper implementations of SOP.
5.0 Abbreviations:
-
- GIM: Goods Inward Memo
-
- AR. No. : Analytical Report Number
-
- FEFO: First Expiry First Out
-
- FIFO: First In First Out
-
- M.R.O. : Material Requisition Order
-
- QA: Quality Assurance
-
- P. M.S.: Packing Material Store
-
- R.M.S.: Raw Material Store
6.0 Procedure – Good Warehousing Practices:
-
-
Receipt and identification of Raw Materials/Packing material. (Good Warehousing Practices)
- A responsible staff member of the raw material department should take the delivery of raw materials/Packing material after proper checking of the description of the material against the description given in the purchase order.
-
-
- All the units of the consignment should be properly labeled by the manufacturer/suppliers.
-
- Every consignment of raw materials must be entered into a Receipt cum Inspection report and must be identified by giving code numbers.
-
- These code numbers should not be repeated.
-
- The name recorded against the code number for the material should be the name by which such material is referred in all documentation within a company.
-
- It is likely that some materials may be either described by a synonymous name on the container or by a brand name.
-
- This may be indicated additionally in a separate column.
-
- The following additional information must be recorded in addition to indicating the code number and the name of the material in the receipt cum inspection report.
-
-
- Date of Receipt
-
-
-
- Name of manufacturer/supplier
-
-
-
- Quantity received
-
-
-
- Invoice challan number and date & then prepared goods inward memo in computer.
-
-
- The following information must be labeled on each container of a consignment of raw material /packing material received after preparing GIM.
-
-
- The serial number of the receipt.
-
-
-
- The standard name of the material as referred to in the company.
-
-
-
- The total quantity of the material received.
-
-
-
- The total number of containers received.
-
-
-
- Quantity of the material in each container.
-
-
-
- Name of Manufacturer/Supplier
-
-
-
- Manufacturer Batch Number, Manufacturing Date, and Expiry Date
-
-
-
- Date of Receipt.
-
-
- Each container of material received in RMS must have a label stating “QUARANTINE/DO NOT USE” OR any such expression.
-
- Such expression on containers indicates that the material is under quality approval.
-
-
Storage of Raw materials/Packing Material: (Good Warehousing Practices)
-
-
- The following are the most important factors that should be taken into consideration while storing a consignment of raw material.
-
- The material must be stored in the storage area depending upon the instruction contained in the raw materials specifications.
-
- All the materials received must be stored in a quarantine area prior to quality approvals.
-
- Each material should be placed at a particular place that has a location code number.
-
- This code number should be entered in the system while preparing GIM
-
- The entry to the RMS must be controlled by permitting only authorized personnel.
-
- The highly potent material is handled by the responsible warehouse personnel.
-
- After quality control release, the material must be moved into the approved area to the particular place which has a locational code number.
-
- This location code should be updated by store personal only after Q.C Approval.
-
- The procedure should ensure that the warehouse personnel knows where each lot of raw material is kept and facilitate their issue on a “FEFO” Basis. (First Expired First Out).
-
- In case of non-availability of location code, the deviation should be authorized by Quality personnel.
-
Cross-contamination – Raw Materials: (Good Warehousing Practices)
-
- Cross-contamination can take place on account of reasons as given below:
-
- When the container of material not closed properly and therefore contamination through the opening by another material in the form of dust or splash or any other accidental means.
-
- Liquid material stored may be leaked on to dry material stored in lower racks must not be stored on the higher racks.
-
- The powder containers stored which would get damaged and thereby produce dust.
-
- They must be stored in such areas that they do not contaminate other raw materials.
-
- Before opening the lid of the container, the Lid must be cleaned properly in order to avoid the transfer of foreign particles while sampling or issue.
-
- Extra precautions must be taken for certain raw materials that have a tendency to promote microbial growth while sampling and issue of the same.
-
- It is more important to take care of closing a container before and after the withdrawal of the contents to prevent cross-contamination.
-
-
Issue of materials: (Good Warehousing Practices)
-
-
- The issue of material must be done in the accordance with work order issue (pick up the list) required for manufacturing.
-
- Special care must be taken in case of issuing potent and light-sensitive materials to prevent any mishap.
-
- Extra precautions are required while handling hazardous materials which include the use of personal safety equipment such as eye protection, hand protection, foot protection, or body protection.
For example, Electrical earthing in case of solvents to prevent fires due to static electricity. The precautions needed must be followed without exception.
-
- After issuing each active material, the unit of that material should be properly closed, and the dispensing area should be cleaned to avoid cross-contamination.
-
PROCEDURE – PARTLY DISPENSED MATERIAL CONTROL:
-
-
Raw Material (Good Warehousing Practices):
-
-
- While dispensing of raw materials, the material having near expiry among the available A.R.Nos. shall be consumed on first priority.
-
- It shall be ensured that material has picked as per FEFO (First Expiry First Out) method in M.R.O.
-
- If the material of the same batch no. received later in that case material to be dispensed as per FIFO (First in First Out) method.
-
- During dispensing take one material inside the dispensing booth and dispense the required loose quantity from the intact container as per the quantity mentioned on M.R.O.
-
- After dispensing from following type of containers, affix the loose label on each loose container as per annexure-1
-
- During dispensing from the fiber drum, plastic drum, and corrugated box, dispense the required loose quantity from the intact containers.
- After dispensing close the inner polybag tightly and tie the polybag with a cable tie and record the material transaction on the loose label(Annexure-1) and affix the loose label on the remaining loose container.
-
-
During dispensing from plastic bag and paper bag, dispense the required loose quantity from an intact bag.
-
-
- Then close the inner polybag tightly and tie it with a cable tie, followed by tying the outer bag with a cable tie.
-
- After completion of the activity record the material transaction on the loose label(Annexure-1) and affix the loose label on the yellow card and tie it with the bag.
-
- During dispensing from the corrugated box of the capsule, dispense the required loose quantity from the intact bag.
-
- After dispensing close the inner polybag tightly and tie it with a cable tie, keep the bag in another polybag.
-
- Tie the outer polybag with a cable tie keeps the polybag in the mother corrugated box and record the material transaction on the loose label(Annexure-1) and affix it on the loose mother container.
-
- After dispensing keep the loose container in its original location in R.M.S.
-
- Next time when the same material with the same A.R.No. is required for dispensing, first, collect the loose container from the material rack, and dispense the required quantity.
-
- Similar practice shall be followed during the handling of loose containers until the total consumption of the material.
-
- It shall be avoided to the creation of more than one loose container of a particular A.R.No.
-
- This is allowed only when the same A.R.No. is required to be dispensed in other dispensing booths.
-
- If required after completion of the first copy of the loose label, take the print off another copy and affix it beside the first label without hidden the records.
-
-
Packing Material – (Good Warehousing Practices) :
-
-
- While dispensing of packing materials, it shall be done as per FIFO (First in First Out) method.
-
- During dispensing of the show box and packing insert, open the intact container, dispense the required loose quantity as per qty. mentioned on M.R.O.
-
- After dispensing close the inner polybag and pack the remaining loose box with plain cello tape and record the material transaction on the Remaining Qty. label and affix the label on the remaining loose container.
-
- After dispensing of required qty. of packing material of show box, packing insert, keep the material in it’s the original location in P.M.S.
-
- Next time when the same material with the same A.R.No. is required for dispensing, first, collect the loose container from the material rack, and dispense the required quantity.
-
- Similar practice shall be followed during the handling of loose containers until the total consumption of the material.
-
- During dispensing of foils, it shall be issued to production as such roll.
-
- After completion of batch picking, the foils shall be returned to P.M.S. by production after proper reconciliation and with a material return label in which the remaining quantity shall be filled properly.
Annexure1: Format for Loose Label.
********************************************************END***********************************************


