 Standard Operating Procedure (OOS) for the handling of Out of Specification Test Results, This SOP is designed based upon MHRA and WHO guideline for Handling of Out of Specification (OOS) results.
Standard Operating Procedure (OOS) for the handling of Out of Specification Test Results, This SOP is designed based upon MHRA and WHO guideline for Handling of Out of Specification (OOS) results.
In the SOP, Detailed procedure provided for the handling of out of specification (OOS) test results, preliminary investigation, Phase I, Phase II and Phase III investigation, cross-functional investigation, and hypothesis study.
SOP for Handling of Out of Specification (OOS) Test Results
1.0 PURPOSE :
-
- To define the procedure for the investigation of out of specification results for the drug products analyzed in the quality control department.
2.0 SCOPE :
-
- This SOP is applicable to all the Out of Specification (OOS) results generated in the quality control department at Pharmaceuticals drug manufacturing plant.
-
- Out of Specification (OOS) investigation shall be initiated for samples (irrespective of sample category), which are analyzed and assessed against approved effective specifications.
-
- Process optimization batch sample (non-commercial), characterization batch sample, developmental stages samples which are required to establish process parameters and assessed against specific protocol limits, shall not be considered under Out of Specification (OOS) investigation scope.
-
- For tests where additional testing criteria are given in the Pharmacopoeia (like Dissolution, Content Uniformity etc.), the analysis shall be done as per Pharmacopoeia. If the sample fails as per Pharmacopoeial criteria, then the sample shall be considered under the scope of Out of Specification (OOS) investigation.
3.0 REFERENCES :
-
- The USFDA Guidance for industry: Investigation out of specification (OOS) test results for pharmaceutical production, October 2006
-
- EU guidance: Good manufacturing practices
-
- MHRA guidance for out of specification investigation, 2013
4.0 RESPONSIBILITY:
-
-
Analyst:
-
-
- Ensure that the instrument used for analysis is calibrated.
-
- Check the data for compliance with approved specifications before discarding test preparations or standard preparations.
-
- Immediately inform the Out of Specification (OOS) results to the section head / Head QC or designee and shall not discard sample solution/stock solution/instrument settings until the evaluation of failure analytical results.
-
- Participate in the investigation, participate in finding the root cause and carry out the experimental analysis where applicable.
-
-
Section head or Designee :
-
-
- Carry out the investigation of Out of Specification (OOS) result as per approved effective SOP’s.
-
- Verify that correct standard, reagent, the chemical used in analysis and review of analyst training and performance record.
-
- Review historical data of laboratory investigation during the initial assessment to determine if similar failures have occurred previously, what were the corrective action and preventive actions and the effectiveness of CA and PA.
-
- Verify the calculation, volumetric solution preparation, HPLC integration. etc.
-
- Interview analyst with OOS investigation form (Phase-I) to find out the root cause.
-
- Discuss with subject matter expert, Review Raw Data, analytical method validation report, method transfer report, and forced degradation data to find the root cause.
-
- Based on the above review he has to prepare a hypothesis/simulation study protocol and plan the study as per approved protocol to find out the root cause or assignable cause for Out of Specification (OOS) results.
-
- Prepare an investigation report based on laboratory investigation.
-
- Initiate the actions recommended in the OOS investigation form.
-
- Determine CA and PA based on assignable cause, performing impact assessment, risk assessment, and training (if required).
-
- To evaluate the impact of Out of Specification (OOS) results on other lots and products.
-
-
Head QC or Designee:
-
-
- Provide guidance for investigation.
-
- Provide guidance for the hypothesis/ simulation study to find out the root cause for
-
- Review and approve the hypothesis/ simulation study protocol prior to the execution of investigational testing and the final report.
-
- Determine CA and PA based on assignable cause, performing impact assessment, risk assessment, and training (if required).
-
- Initiate the actions recommended as CA and PA in the investigation form.
-
- Review, conclude and approve the Out of Specification (OOS) reports.
-
- Periodic review of Out of Specification (OOS) trend and evaluation of the effectiveness of CA and PA derived based on the OOS investigation trend.
-
- Evaluate the impact of Out of Specification (OOS) results on other lots and products.
-
-
QA of QC / Lab QA / GLP Team :
-
-
- Register the Out of Specification (OOS) details in out of specification investigation form issuance logbook as per the SOP.
-
- Issue the Out of Specification (OOS) investigation form.
-
- Review the Out of Specification (OOS) investigation report.
-
- Execute the CA and PA recommended in Out of Specification (OOS) investigation form and closing of the OOS.
-
- Perform periodic trending and review of Out of Specification (OOS) investigation and evaluation of the effectiveness of CA and PA derived based on OOS investigation trend.
-
- Send all kinds of Out of Specification (OOS) related data from location to outside as and when required.
-
-
Head QA or designee :
-
-
- Ensure that investigation shall be performed as per approved effective SOP’s.
-
- Review and approve the Out of Specification (OOS) investigation form.
-
- Carry out a cross-functional investigation.
-
- Based on the review, if required QA can revise the scope of CA and PA, Impact assessment and Risk assessment.
-
- Authorize re-sampling as and when if required.
-
- Conclude Out of Specification (OOS) investigation and approve the OOS investigation form.
-
- Ensure compliance of CA and PA recommended in the OOS investigation form.
-
- Ensure appropriate resources are allocated for conducting timely and effective investigations
-
- Intimation to the regulatory department, ADD, FDD, CQ, RA, and Customer wherever required.
-
- Contract Testing Laboratory:
-
- In the case of Out of Specification (OOS) result generated at the contract laboratory, the contract laboratory shall communicate its analytical data, findings and supporting documentation to the quality control manager on an immediate basis for further assessment.
-
- The manager shall take immediate corrective action based on instructions available in approved effective SOP and discussion with plant Quality head or designee.
5.0 ABBREVIATIONS:
-
- ADD: Analytical Development Department
-
- CA: Corrective Action.
-
- CQ: Corporate Quality.
-
- OOS: Out of Specification.
-
- FDD: Formulation Development Department.
-
- FAR: Field Alert Report.
-
- FDA: Food and Drug Administration.
-
- FMEA: Failure Mode Effective Analysis.
-
- HPLC: High-Performance Liquid Chromatograph.
-
- LOD: Loss on Drying.
-
- PA: Preventive Action.
-
- QP: Qualified Person.
-
- SME: Subject Matter Expert.
6.0 DEFINITION – SOP FOR HANDLING OUT OF SPECIFICATION (OOS):
-
- Out of Specification (OOS): Test results that fall outside the established approved specification limits and or acceptance criteria.
-
-
Assignable cause:
-
-
- A cause (root cause) that has been identified as a reason for Out of Specification (OOS) results.
-
- The assignable cause is a conclusion derived from direct or indirect evidence found during the investigation process, from the interpretation of analytical data or a combination of both.
-
- If the root cause is established as a laboratory error, the OOS data shall be reported as invalid.
-
-
Investigation:
-
-
- Review and experiments jointly conducted by an investigator (team of SME’s) and the analyst to find the root cause attributing to Out of Specification (OOS) results.
-
- This could be a Laboratory (Phase-I) and/ or Cross-functional Investigation (Phase-II).
-
- This should be thorough, timely, unbiased well documented and scientifically sound.
-
-
Retesting:
-
-
- Testing of Portion of the original sample.
-
- The sample used for the retesting should be taken from the same homogeneous material that was originally collected from the lot, tested and yielded the Out of Specification (OOS) results.
-
- For a liquid or single-use formulation pack, it may be from the original unit product or composite.
-
- For a solid, it’s to be an additional weighing from the same sample composite prepared for the original test.
-
- This may include the preparation of fresh standards and/ or other test reagents as appropriate (as per approved effective ATP).
-
- Re-sample: A new sample from the original container where possible, required in the event of insufficient material remaining from the original sample composite or proven issue with original sample integrity.
-
- CA (Corrective Action): Action to be taken to correct the cause and avoid the re-occurrence.
-
- PA (Preventive Action): Action to be taken to avoid the occurrence.
-
-
Hypothesis / Simulation Study:
-
-
- The structured documented sequence of experiments which are designed to identify the root cause for the failure.
-
- This shall be based on a series of discussions, thought processes and scientific rationales’ focused on what might have occurred to yield the Out of Specification (OOS) results.
-
- Each Experiment shall have the pre-defined expectations that actually what outcome we want to observe through that particular experiment.
-
- Investigational tools can be used to design Hypothesis / Simulation protocol i.e. five whys?; Cause and Effect Diagram; FMEA; Fish Bone diagram etc.
-
-
Cross-Functional investigation:
-
-
- The cross-functional investigation includes all the departments that could be implicated (e.g. Manufacturing process, Development, Maintenance, Engineering, etc.) in the Out of Specification (OOS) results.
-
- This process to investigate the Out of Specification (OOS) failure thorough a review of the manufacturing process, conditions, input materials and it’s documentation.
-
- Raw Material: A general term used to denote starting materials, reagents, excipient and solvents intended for use in the production of intermediates, drug substance or drug products.
7.0 PROCEDURE FOR HANDLING OF OUT OF SPECIFICATION (OOS) RESULTS:
-
-
General requirement and guideline for Out of Specification (OOS) investigation:
-
-
- The purpose of the investigation is to identify the root cause for the Out of Specification (OOS) results. The investigation shall be thorough, timely, unbiased, well documented and scientifically sound.
-
- If the root cause of Out of Specification (OOS) results are not established, then batch (and any other batches determined to be under the scope of the investigation) shall not be released for the next step.
-
- The OOS investigation shall include a list of all lots in the scope of OOS investigation and why they are considered to be the scope of the investigation.
-
- The further decision of batch disposition shall be decided by Head Quality based on the review of product history, other tests and stages result of the same batch.
-
- Initial Out of Specification (OOS) results can be disregarded, only if the assignable cause is established as laboratory error, sampling error and is not assignable to manufacturing and process related error.
-
- Initial Out of Specification (OOS) results shall not be replaced with retest result if,
-
-
- Any individual result doesn’t meet the specification limit.
-
-
-
- The average result doesn’t meet the specification limit.
-
-
-
- % RSD of replicate retest results doesn’t meet the acceptance criteria defined in Annexure-6.
-
-
- Investigational testing results (hypothesis/ simulation study results) shall not be used to replace an original Out of Specification (OOS) results. It is only to confirm or discount a probable cause.
-
-
Batch rejection does not negate the need to perform the investigation for the identification of the root cause of the Out of Specification (OOS).
-
-
- Even if a batch is rejected based on an Out of Specification (OOS) result, an investigation is necessary to establish the root cause.
-
- When the root cause is identified, the scope of the investigation shall include all other batches manufactured or in the process that may be associated with the identified root cause.
-
- Appropriate action shall be taken by QA to ensure that these batches are appropriately investigated and dispositioned.
-
- After identifying the root cause, this root cause has to be established as assignable cause through experiment and challenging the root cause identification.
-
- The analyst should be aware of potential problems that could occur during the testing process and should watch for problems that could create inaccurate results.
-
- Analysts should not knowingly continue any analysis which he or she expects to invalidate at a later time for an assignable cause.
-
- If such a problem or issue is suspected or encountered it shall be reported immediately to the section head or designee.
-
- If Out of Specification (OOS) results observed, the analyst shall not discard sample solution/stock solution/instrument setting until the evaluation of failure analytical results.
-
- In case the solution is not stable (based on Analytical Solution Stability study) then the further investigation can be performed by new sample preparation with appropriate justification.
-
-
The expired solution may be used in hypothesis/investigational testing if needed to find out the assignable cause based on proper justification.
-
-
- In the absence of any analyst involved in the investigation, Head QC or designee can assign the task to another analyst after authorization.
-
- At any stage, if the sample is not available for further investigation, a re-sample shall be carried out with proper justification to performed further investigation.
-
- Any other lots or batches analyzed in same sequence implicated in the error contributing to the Out of Specification (OOS) results shall be under the scope of Out of Specification (OOS) investigation (impact assessment) unless removal from scope shall be justified in writing by Head QC or designee and authorized by Head QA or designee.
-
- Every step shall be fully documented and records shall be preserved as a part of the laboratory data.
-
- Based on the assignable cause identified, impact assessment of other batches analyzed in the same sequence, other batches tested by the same analyst, instruments, etc. shall be evaluated and retesting in single time shall be performed, unless justified in writing by Head QC and Head QA/Head Quality.
-
- Impact assessment and risk assessment shall be an integral part of Out of Specification (OOS) investigation form.
-
-
Out of Specification (OOS) Investigation Procedure:
-
-
- When out of specification results obtain, the analyst shall immediately report to section head or designee and shall not discard sample plates, Benchtop solutions until the evaluation of failure results.
-
- Section head or designee shall take actions as described below.
-
-
Out of Specification (OOS) Investigation (Phase-I):
-
Flowchart-Out of Specification (OOS)-Phase I
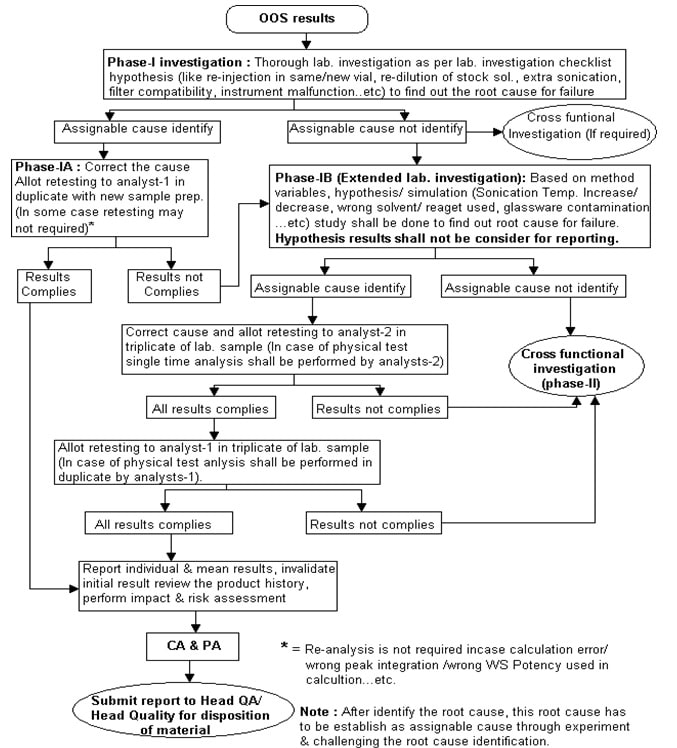
-
- In case of observation of Out of Specification (OOS) results, analysts (Analyst-1) shall report to section head or Designee on same day or as immediately as possible.
-
- Section head or Designee shall inform to QA of QC. The designated person of QA of QC shall take the following actions,
-
- Issue “Out of specification investigation form (Phase-I)” (Annexure-2) to the analyst and make relevant entries in the “Out of specification investigation form issuance logbook” (Annexure-1) and “Out of specification investigation form (Phase-I)” (Annexure-2).
-
- Out of Specification (OOS) Form No. shall be given as OOS/YY/XXX,
-
-
- Where, OOS = Out of specification
-
-
-
- YY = Last two digits of the current year
-
-
-
- XXX= Serial No, (e.g. 001,002….etc.)
-
-
- Thus the first OOS Form No. in 2020 shall be given as OOS/20/ 001.
-
- Section head or designee shall carry out the investigation as per the checklist provided in the Out of Specification (OOS) investigation form (but not limited to checkpoint given in checklist). Benchtop audit like
-
-
- Glassware used.
-
-
-
- Reagent used.
-
-
-
- Correct pipette and volumetric flasks used.
-
-
-
- Correct labeling of volumetric flask and vial.
-
-
-
- Placement of vial in the autosampler.
-
-
-
- Correct volumetric solution and electrode used.
-
-
-
- Review of the historical trend, Raw data review, discussion with analyst, as a part of investigation to find out the root cause for failure.
-
-
- Section head or designee shall mention the investigation findings and conclusion into “Summary of investigation”.
-
-
Findings shall be reviewed and signed by QA of QC person.
-
-
- Section head or designee shall plan initial hypothesis (Examination of retained solution like the final solution in the same vial/ new vial, re-dilution of stock solution, extra sonication, filter compatibility if no assignable cause is found through checklist review, raw data review, analyst discussion and benchtop audit, etc.
-
- Based on finding’s (checklist review, raw data review, review of the historical trend, analyst discussion, benchtop audit and initial hypothesis study i.e. examination of retain solution), if assignable cause found to be laboratory error then performed the Phase-IA investigation and if assignable cause is not found then follow investigation procedure define in Phase-IB.
-
-
Phase-IA Investigation (If the assignable cause of laboratory error is found based on the checklist/initial hypothesis study) :
-
-
- Based on the assignable cause identified (checklist review, raw data review, review of the historical trend, analyst discussion, benchtop audit / or initial hypothesis i.e. examination of retained solution), section head or designee shall decide further investigation as under,
-
- Section head or designee shall instruct analyst-1 to correct the cause and perform retesting of the sample in duplicate with new sample preparation.
Note: Retesting (repeat analysis) is not required in case of Out of Specification (OOS) results generated due to reporting error i.e. calculation error/ wrong peak integration/ wrong WS potency used. etc., in such cases correct the cause and report the result.
-
- Report the retest results into the Out of Specification (OOS) investigation form and conclude as follow,
-
- If all individual and mean results comply with the specification limit, review the product history, invalidate the initial results, perform impact and risk assessment and identify the CA and PA. Document CA and PA and training, if needed, in the Out of Specification (OOS) form. Submit the report to Head QC and Head QA/Head Quality for the closing of OOS investigation and disposition of material.
-
- If any result (individual or average result) does not comply with the specification limit, then performed further investigation as per procedure define in Phase-IB investigation.
Note: If required, Head QC and Head QA can decide to initiate the cross-functional investigation parallel to the Phase-IB investigation to save investigation time.
-
-
Phase-IB (If the assignable cause is not found based on checklist/initial hypothesis study) extended lab. investigation:
-
-
- Hypothesis /Simulation study protocol shall be designed in discussions with SME’s, analysts and reviewers.
-
- The analytical procedure defined in ATP’s and analysis performed by the analyst (based on Interview of analyst) shall be discussed in detail to find out the variables which can lead to Out of Specification (OOS) results.
-
- Identification of variables can further be extended through a review of analytical validation documents (force degradation data), analytical method transfer data and other relevant discussion and data review available with ADD (Developmental data).
-
- Section head or designee shall plan the hypothesis/ simulation (like sonication temperature increase or decrease, wrong solvent/ reagent used, glassware contamination, etc. based on variables identified study through an approved protocol to find out the root cause for failure (Refer to Annexure-4, for the guidance of hypothesis/simulation study).
-
- Experiments planned in hypothesis/simulation protocol shall have a predefined objective.
-
- Section head or designee shall review the hypothesis/ simulation study data and if assignable cause identify based on the hypothesis/ simulation study, shall recommend retesting of the sample as outlined below,
- Section head or designee shall allot the retesting of the sample to analysts-2 in triplicate with new sample preparation.
Note: In the case of physical test, analyst-2 shall analyze the sample a single time and report the result.
-
- The following test shall be considered as a physical test but not limited to,
-
-
- Description,
- Solubility,
- Bulk density,
- Sieve analysis,
- Particle size analysis,
- Hardness,
- Weight variation,
- Uniformity dosage units by weight method,
- loss on drying,
- Water content,
- melting point/ range,
- Color and clarity test,
- Residue on ignition.
-
-
- Report the results in out of specification investigation form (phase-I) and conclude as follow,
-
- If all results (individual and average of three results) comply with the specification limit and acceptance criteria define in Annexure-6, then section head or designee shall allot the retesting of sample to analysts-1 in triplicate with new sample preparation.
Note: In the case of a physical test, analyst-1 shall analyze the sample in duplicate and report the results. The average result of analyst-2 and analyst-1 shall be considered for reporting (wherever applicable).
-
- Report the results of analyst-1 in Out of Specification (OOS) form and conclude as follow,
-
- If all results (individual and average of three results) comply with the specification limit and acceptance criteria define in Annexure-6 and then take the average of six results (analyzed by analyst-2 and analyst-1) and report.
-
- If the average of six results comply with the specification limit and acceptance criteria define in Annexure-6, review the product history, perform impact and risk assessment and identify the CA and PA.
-
- Document the CA and PA in Out of Specification (OOS) form and submit the report to Head QC and Head QA/Head Quality for the closing of Out of Specification (OOS) investigation and disposition of material.
-
- Any results (Individual results of analyst-2, analyst-1 or average results) does not comply with the specification limit or acceptance criteria defined in Annexure-6, then conclude the Phase-IB laboratory investigation and submit the report to Head QC, Head QA/ Head Quality for review and intimate to QA to initiate cross-functional Out of Specification (OOS) Phase-II investigation.
-
-
If any assignable cause is not identified based on hypothesis/ simulation study then intimate to QA to initiate cross-functional Out of Specification (OOS) Phase-II investigation.
-
-
- In case no laboratory error is identified in Phase-IA investigation and failure result is obvious and acceptable based on historical similar failures (Same product, same manufacturing process, same test, with same analytical method) for which thorough Out of Specification (OOS) investigation up to Phase-II is performed earlier and or root cause is established, extended analytical investigation Phase-IB and Phase-II investigation can be discontinued and laboratory investigation can be closed.
-
- Previous Out of Specification (OOS) investigation/event shall be cross-referenced. Section head or designee shall ensure that all information in the previous investigation applies to this sample and batches under the scope of investigation shall be dispositioned by QA designee.
-
- Scientific rationale/Justification for not performing of Phase-IB and Phase-II investigation shall be mentioned in the Out of Specification (OOS) investigation form.
-
-
Full -Scale Investigation (Phase-II) – Out of Specification (OOS):
-
Flowchart-Out of Specification (OOS)-Phase II
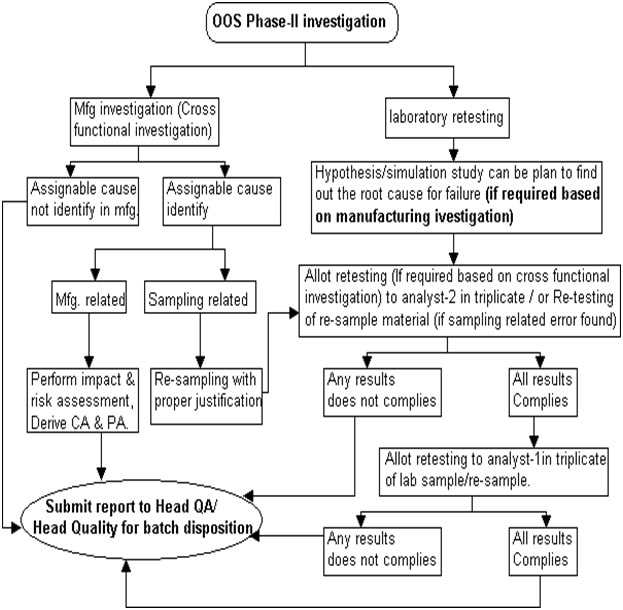
-
- From phase-I laboratory investigation, when laboratory error remains unidentified, issue Out of Specification (OOS) investigation form (Phase-II) (Annexure-3) and intimate to QA for cross-functional investigation as per SOP on “Event reporting and investigation” / Incident.
-
- Note: If required section head or designee shall plan additional Hypothesis/Simulation study to support the manufacturing investigation and to find out the root cause of failure. Experiments planned in hypothesis/simulation protocol shall have a predefined objective.
-
- If Out of Specification (OOS) results for raw material and packaging material is confirmed then plant Head QA/Head Quality shall communicate to the vendor through purchasing departments for further investigation at vendor end.
-
- Reduce testing program shall be discontinued, if the material is on reduce testing program.
-
- Complete analysis for the future consignment shall be performed until adequate corrective is provided by the vendor.
Related: SOP for Vendor Management in Pharmaceuticals
-
- The previous consignment analyzed under the reduce testing program shall be reviewed.
-
- During the cross-functional investigation, if the assignable cause is attributed to as sampling error, re-sampling shall be allowed with proper justification.
Related: SOP for Sampling of Raw Material
-
- Head QC or designee shall provide justification for re-sampling and re-sampling quantity in the “Material re-sample authorization” section of the Out of Specification (OOS) investigation form and obtain approval from Head QA/ Head Quality.
-
-
Re-sampling shall be done for the investigation in the following cases also but not limited to,
-
-
-
- If the original sample exhausted.
-
-
-
- A sample handling error is identified.
-
-
-
- To perform any hypothesis/simulation study.
-
-
-
- To confirm the contamination of the sample.
-
-
- After re-sampling section head or designee shall allot the retesting to analyst-2 and analyst-1.
-
- If after cross-functional investigation, the assignable cause is identified as related to manufacturing, process or any other cause then the decision for disposition (rejection or further investigation) of batch shall be subjected to the approval of Quality Head or designee.
-
- Based on the nature of the assignable root cause, impact assessment on other batches of the same product and other products shall be performed and corrective action and preventive action shall be mentioned in the investigation form.
-
- If after cross-functional investigation, there is no assignable cause found and there is no confirmation for sampling error, then Head QA/ Head Quality shall make the decision for final disposition of material and FDA notification shall take place as required by regulatory agencies.
-
-
For Dissolution/Drug release :
-
-
- If first analysis result indicates that product does not meet the S1+S2+S3 criteria (For ACC stability study S1+S2 criteria ) or significant higher side or lower side (aberrant) results observed within analysis then assign Out of Specification (OOS) for preliminary investigation and
-
- In the case, the assignable cause is not found then reanalysis with 12 units (2 sets) by analyst-2. If results found satisfactory consider for reporting.
Related: SOP for Out of Calibration (OOC)
-
- However the reason for invalidating initial results to be investigated and recorded.
-
- If results found unsatisfactory, proceed for cross-functional investigation or further action shall be decided by Head Quality.
-
-
For Uniformity of dosage unit (CU) :
-
-
- If first analysis result indicates that product does not meet the L1 + L2 (for n =30) criteria or significant higher side or lower side (aberrant) results observed within analysis then assign Out of Specification (OOS) for preliminary investigation and
-
- In the case, the assignable cause is not found then reanalysis with 20 units (2 sets) by analyst-2. If found satisfactory consider for reporting.
-
- However, the reason for invalidating the initial result shall be investigated and recorded. If found unsatisfactory, proceed for cross-functional investigation or further action shall be decided by Head Quality.
-
- Based on the Out of Specification (OOS) investigation and it’s findings corrective action / preventive action and CAPA number (if required) shall be mention under the “Recommended corrective/ preventive action” section of the OOS investigation form to avoid re-occurrence of the error.
-
-
Retesting :
-
-
- Based on the cross-functional investigation, if required laboratory retesting by analyst-2 and analyst-1 can be performed but the final decision for batch release shall be made based on the outcome of cross-functional investigation only.
-
- The purpose of this retesting is to replace the erroneous (invalid) results in the first analysis if the assignable cause is not related to any manufacturing or process-related error.
-
- Retesting shall be performed by analyst-2 and analysts-1 as per procedure defined in the Phase-IB investigation.
Related: SOP for Out of Trend Test Results (OOT)
-
- Report the retest results into Out of Specification (OOS) form and submit the retest results to Head QA and Head Quality for closing Out of Specification (OOS) investigation.
-
- The final decision of batch disposition shall be decided by Head QA/Head Quality, based on the outcome of laboratory investigation, cross-functional investigation, review of product history, other test results of the same batch and impact and risk assessment.
-
-
Blend Uniformity investigation:
-
-
- When BU results do not meet the specification limit then preliminary laboratory investigation shall be performed as per procedure defined at OOS Investigation – Phase I.
-
- Based on the above investigation, if assignable cause found then perform Phase-I investigation and if the assignable cause is not found then follow the investigation procedure define in Phase-II.
-
-
Blend Uniformity Phase-I investigation:
-
-
- Section head or designee shall instruct the analyst to correct the cause and retest the second set of BU samples.
-
- Note: Retesting is not required in case of failure result generated due to reporting error i.e. calculation error/ wrong peak integration /wrong WS potency use, In such cases correct the cause, report the corrected results and mention the root cause, CA and PA and other steps given in Out of Specification (OOS) form.
-
- Report the retest results into the Out of Specification (OOS) investigation form and conclude as follows,
-
- If results (individual and mean) meet the specification limit, review the product history, invalidate the initial results, perform impact and risk assessment and identify the CA and PA.
-
- Document CA and PA and training, if needed, in the OOS form.
-
- Submit the report to Head QA for the closing of OOS investigation and disposition of material.
-
- If any individual or mean results do not meet the specification limit. Perform further investigation as procedure define in Blend Uniformity (Out of Specification (OOS) phase –II investigation)
-
-
Blend Uniformity (Out of Specification (OOS) Phase-II investigation):
-
-
- If results do not comply in Phase-I investigation and/or no laboratory error is identified, then intimate to Head QA or designee for a cross-functional investigation.
-
- Based on the cross-functional investigation if the assignable cause is identified then the second set of BU samples shall be retested by analyst-1.
Note: If sampling related error identified, re-sampling shall be done with proper justification and authorization from QA Head/ Quality Head and retesting shall be performed with re-sampled material.
-
-
Report the second set BU results into the Out of Specification (OOS) investigation form and conclude as follows,
-
-
- If results (individual and mean) comply as per specification limit. Review the product history and other test and stage results, perform impact and risk assessment and identify the CA and PA. Document CA and PA and training, if needed, in the OOS form.
-
- Submit the report to Head QC and Head QA/Head Quality for the closing of Out of Specification (OOS) investigation.
-
- Based on the cross-functional investigation if the assignable cause is not identified then perform a hypothesis study through the approved protocol with the second set of BU samples.
-
- Section head or designee shall review the hypothesis study data. If the assignable cause is identified then the third set of BU samples shall be retested by analyst-1.
-
-
Report the third set BU results into the Out of Specification (OOS) investigation form and conclude as under,
-
-
- If results (individual and mean) comply as per specification limit. Review the product history, other tests, and stage results.
-
- Perform impact and risk assessment and identify the CA and PA, Document CA and PA and training, if needed, in the Out of Specification (OOS) form.
-
- Submit the report to Head QC and Head QA/Head Quality for the closing of Out of Specification (OOS) investigation.
-
- The final decision for batch disposition shall be decided by Head QA/Head Quality, based on the outcome of laboratory investigation, cross-functional investigation, review of product history, other tests result of the same batch and impact and risk assessment.
-
- If any results (individual or mean) do not compile the specification limit. Then submit the investigation report to Head QA and Head Quality for further decision.
-
-
Closure of Out of Specification (OOS) investigation:
-
-
- After completion of Out of Specification (OOS) investigation and cross-functional investigation. Head QA or designee shall ensure the necessary attachments are filed with the OOS investigation form.
-
- After review of the OOS investigation/ cross-functional investigation. CA and PA form shall be issued by QA and ensure compliance of CA and PA.
-
- Impacted department Head shall monitor each recommendation mentioned in the OOS form.
-
- Laboratory investigation shall be completed within 30 days from the date of out of specification result.
-
- Out of Specification (OOS) investigation (Including all investigation i.e Laboratory and Cross-functional) shall be completed within 45 calendar days from the date of occurrence of OOS result.
-
- Out of Specification (OOS), the investigation shall not be closed until the laboratory and Cross-functional investigation is not completed.
-
- If Out of Specification (OOS) investigation requires more time for closing than the defined period i.e. 45 days.
-
- Then the extension of closer shall be obtained and approved by Head QC and Head QA prior to the due date.
-
-
An interim report shall be prepared for an extension of closure.
-
-
- The interim report shall have proper justification for extension and an impact assessment for the Out of Specification (OOS).
-
- Report shall include a re-assessment of the batches in the scope of the investigation. The interim report shall be approved by Head QA/Head Quality.
-
- The extension can be given for one month from the date of the request for the extension.
-
- In any case, the extension time period shall not be exceeded more than 75 days from the date of occurrence of the out of specification results.
-
- Human errors shall be trended on a quarterly basis and CA and PA shall be derived to avoid repetitive human errors.
-
- Human errors shall be addressed as per the guidelines provided in Annexure-6 (but not limited to).
-
-
Trending and Evaluation of Out of Specification (OOS):
-
-
- Trending and evaluation of Out of Specification (OOS) shall be carried out on a quarterly basis by QA of QC.
-
- QA of QC shall review the data and evaluate the repetitive type failures as per following but not limited to,
-
-
- 1) Repetitive failure in a particular test of the product
-
-
-
- 2) Repetitive failure by particular analyst
-
-
-
- 3) Repetitive failure of any stage of product sample etc.
-
-
-
- 4) Repetitive failure on the particulate instrument.
-
-
- For Example – Total no. of Out of Specification (OOS) generated 31 in three months and cause of failures are as below,
-
- a) Glassware and HPLC vial contamination – 6 nos.
- b) Wrong glassware used -4 nos.
- c) Storage condition of the sample not maintained -5 nos.
- d) Specific test wise -3 nos.
- e) Analyst wise -4 nos.
- f) Product-wise -5 nos.
- g) Instrument (HPLC/GC/IC etc.) – 4 nos.
-
- QA of QC shall prepare the graph (Bar type) for causes of failure (X-axis) against the number of Out of Specification (OOS) results generated (Y-axis).
-
- QA of QC shall analyze the repetitive failure (s) from data and identify training/corrective and/ or preventive action required.
-
- Effectiveness checks for training or other CAPAs shall be evaluated to confirm the reduction in error.
-
- The further action plan shall be derived based on the evaluation of the effectiveness check (if required).
-
-
Handling of Out of Specification (OOS) at contract testing laboratory:
-
-
- In the case of an Out of Specification (OOS) result generated at the contract laboratory. An Out of Specification (OOS) investigation shall be carried out by the contract laboratory.
-
- The contract laboratory shall convey its data, findings and supporting documentation to the plant’s quality control unit.
-
- The further strategy shall be decided by the plants Quality Control Unit/Head Quality.
8.0 ANNEXURES :
Annexure – 1: Out of specification investigation form issuance logbook
Make the table containing following contents for logbook
-
- Sr. No.
- Product/Item
- Batch Number/ AR Number
- Stage
- Test
- OOS Form No.
- Details of the OOS Investigation form. ( Phase-I)
- Issue to
- Issue By / Date
- Received By / Date
- Details of the OOS Investigation form. (Phase-II)
-
-
- Issue to
- Issue By / Date
- Received By / Date
- Status of OOS (Open/ Close)
- Event No. (if any)
- CAPA No. (if any)
- Remarks (If any)
-
Annexure – 2: Out of specification investigation form (Phase-I)
| Form No. | : | Issued by | : | ||
| Issued to | : | Date | : | ||
| Ref. OOS No. (CTL) | : | Date | : | ||
| Product/Item : | |||||
| Batch No. / AR No. : | |||||
| Stage : | Mfg. Date : | Exp. Date | |||
| Test : | Results : | Limit : | |||
| Analyzed by : | Date : | Reference : | |||
Laboratory investigation-Phase-I (OOS Investigation Checklist)
| Sr. No. | Parameters | Yes | No | NA |
| 1 | Reference record/ document review | |||
| 1.1 | Was the Correct specification followed?
Specification with version No. : ___________ |
|||
| 1.2 | Was correct method of analysis followed. : Method No.:___________ | |||
| 1.3 | Was the method validated ? Method validation Report No. :___________ | |||
| 2 | Sample check | |||
| 2.1 | Was the physical appearance of samples satisfactory? | |||
| 2.2 | Was the sample stored as per the required storage condition? | |||
| 2.3 | Was the labeling adequate? | |||
| 2.4 | Was the correct sample used for analysis? | |||
| 2.5 | Was the sample stored and transported as per the required packaging condition? | |||
| 2.6 | Was there any sample mix-up during storage and handling. | |||
| 2.7 | Was the sampling procedure followed (feedback based on interrogation with concern person) as per respective SOP? | |||
Remarks : ___________________________________________________
|
Sr. No. |
Parameters | Yes | No |
NA |
| 3 | Instruments review | |||
| 3.1 | Balance checked for its calibration.
Code No. of Balance :__________ Code No. of Balance :__________ |
|
||
| 3.2 | Instrument Calibration checked.
(Check as per respective SOP). Name of Instrument :_______ Code No.: _________ Name of Instrument :_______ Code No.: _________ Name of Instrument :_______ Code No.: _________ |
|||
| 3.3 | Was the instrument equilibrated/ cleaned properly before use…? | |||
| 3.4 | Was any instrument/equipment error identified during the investigation? | |||
| 3.5 | Was the instrument working constantly as per requirement…? | |||
4 |
Sample preparation investigation |
|||
| 4.1 | Was the sample / standard solution prepared adequately….? | |||
| 4.2 | When were the standard and sample prepared..? | |||
| 4.3 | Was any abnormality observed in sample vial and syringe penetrates all the vials used in the run…? | |||
| 4.4 | Was the sample / standard solution storage as per the storage requirement? | |||
| 4.5 | Were glassware and instrument used in analysis clean…? | |||
| 4.6 | Was the correct pipette / volumetric flask / other glassware used as per dilution mention in the test procedure? | |||
| 4.7 | Was it checked whether the analyst performing multiple testing simultaneously which cause potential sample mix up? | |||
| 5 | Working/reference standard review | |||
| 5.1 | Was the physical condition of the working/reference standard found satisfactory | |||
Remarks: _______________________________________
|
Sr. No. |
Parameters | Yes | No |
NA |
| 5.2 | Was the validity of the working/reference standard checked?
Code No. of RS/WS: Validity: |
|||
| 5.3 | Was the potency of working/reference standard used as per label claim checked? | |||
| 5.4 | Was the working/ reference standard used correct (like the salt of the base form used)? | |||
| 5.5 | Was reference standard/Working standard stored in proper condition..? | |||
| 5.6 | How long has working standard bottle been in use in the lab? ____ days. | |||
| 5.7 | Was the reference/ working standard dried correctly before use (If required as per ATP/Label claim)
Oven No.:_______ Drying time:______ |
|||
| 5.8 | Was the standard weighed immediately or after reaching the room temperature…? | |||
| 6 |
Chemical/ Reagent / Volumetric solution review |
|||
| 6.1 | Was the proper grade of chemical/reagent used for analysis? | |||
| 6.2 | Was the physical appearance, validity of chemical/ reagent used satisfactorily? | |||
| 6.3 | Is there any specific grade chemical/ reagent use given in ATP? | |||
| 6.4 | Was the physical condition of the prepared solution and raw data of Volumetric Solution satisfactory? | |||
| 6.5 | Was the physical appearance of primary and secondary standards and it’s validity found satisfactory? | |||
| 6.6 | Were the prepared/used solution is within the expiry period?
VS No.: Validity: |
|||
| 6.7 | Was standardization performed adequately? | |||
| 6.8 | Were calculations verified for correctness? | |||
| 7 | Raw data and methodology review | |||
| 7.1 | Were there any deviations from the analytical test procedure? | |||
Remarks: _______________________________________
| Sr. No. | Parameters | Yes | No | NA |
| 7.2 | Are the chromatograms / printouts / TLC plates / spectrum etc. adequate? | |||
| 7.3 | Are the chromatograms properly integrated? | |||
| 7.4 | Was the dilution, weighing, titer values, and readings found satisfactory? | |||
| 7.5 | Was the system suitability checks (HPLC/UPLC/GC) found satisfactory? | |||
| 7.6 | Was the bracketing standard RSD as per the limits? | |||
| 7.7 | Were the calculation and formula used correctly? | |||
| 7.8 | Was any other test performed of the same sample? If so, then results comply the specification limit. | |||
| 7.9 | Was there any evidence of contamination from a previous run /injection? | |||
8 |
Chromatography review. |
|||
| 8.1 | Pump: | |||
| 8.1.1 | Was the flow rate correct? ______ ml/min. | |||
| 8.1.2 | Were any pressure fluctuation observed? | |||
| 8.1.3 | Was any leakage observed? | |||
| 8.1.4 | Was pump primed properly before use? | |||
| 8.2 | Column: | |||
| 8.2.1 | Was the column used as per ATP? | |||
| 8.2.2 | Was any evidence of temperature fluctuation? | |||
| 8.2.3 | What was the column type, serial no? and temperature? | |||
| 8.3 | Detector: | |||
| 8.3.1 | Was the detector functioning properly? | |||
| 8.3.2 | Was wavelength selected as per ATP? | |||
| 8.4 | Mobile Phase (liquid chromatography) | |||
| 8.4.1 | Was the mobile phase prepared properly? | |||
| 8.4.2 | What was the composition of needle wash? | |||
Remarks: _______________________________________
| Sr. No. | Parameters |
Yes |
No |
NA |
|
| 8.4.3 | Was any evidence of air bubbles in the mobile phase during use? | ||||
| 8.5 | Mobile Phase (Gas chromatography) | ||||
| 8.5.1 | Was the correct carrier gas used? | ||||
| 8.5.2 | Was the Flow parameter as per ATP? | ||||
| 8.5.3 | Were detector temperature/ ramp setting as per ATP? | ||||
9 |
Chemical/ Reagent / Volumetric solution review |
||||
| 9.1 | Was the proper grade of chemical/reagent used for analysis? | ||||
| 9.2 | Was the physical appearance, validity of chemical/ reagent used found satisfactory | ||||
| 9.3 | Is there any specific grade chemical/ reagent use given in ATP. | ||||
| 9.4 | Is the physical condition of the prepared solution and raw data of Volumetric Solution found adequate? | ||||
| 9.5 | Was the physical appearance of primary and secondary standards and it’s validity found satisfactory? | ||||
| 9.6 | Were the prepared/used solution is within the expiry period.
VS No.: validity: |
||||
| 9.7 | Was standardization performed adequately? | ||||
| 9.8 | Were calculations verified for correctness? | ||||
| 10 | Analyst Check | ||||
| 10.1 | Was the analyst trained for the analytical technique to perform a particular analysis? | ||||
| 10.2 | Have analysts generated other OOS using the same methodology for the same product and other products? | ||||
| 10.3 | Was the analyst training, qualification and performance record found satisfactory? Training date: |
||||
11 |
Other review |
||||
| 11.1 | Does this laboratory event indicate a repetitive type of event? | ||||
| 11.2 | Are there any OOS/OOT results observed in the previous stability station? | ||||
| 11.3 | If more than one batch tested at the same time/ same sequence, are other results satisfactory? | ||||
| Sr. No. | Parameters | Yes | No | NA |
| 11.4 | Glassware checked for its accuracy i.e. Class A or Class B grade glassware used. | |||
| 11.5 | Environmental temperature/ humidity within the area while the test was performed. | |||
| 11.6 | Was previous batches trend data verify. Same type of event generated in the past. | |||
| 11.7 | Any Other |
| Sr. No. | Summary of discussion points | Remark of Investigator | |
| Analyst sign/date | Section head or designee sign/date | ||
| Results of samples analyzed in the same sequence |
| Summary of the investigation by the investigator (checklist review, raw data review, review of the historical trend, analyst discussion, benchtop audit) : |
| Initial Hypothesis results (Examination of the retained solution in the same vial / new vial of diluted stock solution/ Extra sonication/ filter compatibility): | ||
| Analyzed by/date | Reference documents: | |
| Conclusion of the investigator: | ||
| Section head :
Date: |
Head QA or designee:
Date : |
|
Phase-IA If assignable cause found
| Assignable cause identified based on checklist review, raw data review, review of the historical trend, analyst discussion, benchtop audit and or initial hypothesis i.e. examination of retaining solution. Section head or designee shall instruct the analyst to correct the cause and perform retesting of the sample in duplicate with new sample preparation. | ||||
| Allotted By/ Date: | Allotted To/ Date: | |||
| Result of set-I : | Result of set-II : | |||
| Average Result : | ||||
| Analyzed by : | Date : | Reference : | ||
| Conclusion of Phase-IA: | ||||
| Section head :
Date: |
Head QA or designee:
Date : |
|||
Phase IB (If assignable cause not identified) extended lab investigation:
| PRODUCT/MATERIAL RE-SAMPLING AUTHORIZATION FORM | ||||
| Justification for re-sampling : | ||||
| B No./A.R.No. | Stage of investigation | Quantity : | Authorized by/date( Head QA/Head Quality) | Sampled by: |
| Event/ incident No (if required): | ||||||
| Based on extended laboratory hypothesis study and root cause identified in hypothesis, section head or designee shall allot retesting of sample in triplicate to analyst-2. | ||||||
| Allotted By/ Date: | Allotted To/ Date: | |||||
| Results | ||||||
| Set-I: | Set-II: | Set-III: | ||||
| Average Results : | % RSD : | |||||
| Analyzed by: | Date: | Reference : | ||||
| Conclusion of Phase-IB analyst-2 investigation: | ||||||
| Section head :
Date: |
Head QA or designee:
Date : |
|||||
| All results of analyst-2 complies, section head or designee allot retesting of sample in triplicate to analyst-1. | ||||||
| Allotted By/ Date: | Allotted To/ Date: | |||||
| Set-I: | Set-II: | Set-III: | ||||
| Average of three results : | % RSD : | |||||
| Average of six results : | ||||||
| Analyzed by: | Date: | Reference : | ||||
| Conclusion of Phase-IB investigation: | |
| Rational for the invalid result : | |
| Section head :
Date: |
Head QA or designee:
Date : |
AUTHORIZATION FOR INVESTIGATION TIMELINE EXTENSION |
||||
| No. of extension |
I |
II |
||
| Requested by/date | ||||
| Justification/reason
for extension |
||||
| Actual Target date | ||||
| Extended Target Date | ||||
| Authorized by/date | ||||
| Root Cause : | ||||
| Final Conclusion : | ||||
| Impact assessment : | ||||
| Risk assessment : | ||||
| Corrective action :
(CAPA No.:________ ) |
||||
| Preventive action :
(CAPA No.:________ ) |
||||
| Head QC or designee:
Date: |
Head QA or designee:
Date: |
|||
Annexure – 3: Out of specification investigation form (Phase-II)
| Form No. | : | Issued by | : | ||||
| Issued to | : | Date | : | ||||
| Product/Item : | |||||||
| Batch No. / AR No. : | |||||||
| Stage : | Mfg. Date : | Exp. Date | |||||
| Test : | Results : | Limit : | |||||
| Analyzed by : | Date : | Reference : | |||||
| Full-scale OOS investigation phase-II | |
| Event/incident report No.(if any)__________________ | |
| Section head or designee shall allot retesting of sample to analyst-2 in triplicate if required based on the cross-functional investigation. | |
| Allotted By/ Date: | Allotted To/ Date: |
| Results | |||||||
| Set-I: | Set-II: | Set-III: | |||||
| Average results : | % RSD : | ||||||
| Analyzed by :
|
Date : | Reference : | |||||
| Conclusion of the investigator : | |||||||
| Section head :
Date: |
Head QA or designee:
Date : |
||||||
| All results of analyst-2 are complying, then section head or designee shall allot retesting of sample to analyst-1 in triplicate. | |||||||
| Allotted By/ Date : |
Allotted To/ Date: |
||||||
| Results | ||||
| Set-I: | Set-II: | Set-III: | ||
| Average of three results : | % RSD : | |||
| Average of six results : | ||||
| Analyzed by :
|
Date : | Reference : | ||
| Conclusion of investigator : | ||||
| Section head :
Date: |
Head QA or designee:
Date : |
|||
| MATERIAL RESAMPLE AUTHORIZATION FORM
For the re-sampling follow the procedure defined in respective location SOP (SOP No._____ ). |
||||
| Justification for re-sampling: | ||||
| B No. / AR NO.: | Stage of investigation | QTY.: | Authorized By/Date:
(Head QA/Head Quality) |
Sampled By/Date: |
|
|
||||
| Rational for the invalid result : | |
| Section head :
Date: |
Head QA or designee:
Date : |
Annexure – 4: Guidance for Hypothesis/ Simulation study
Some example of Hypothesis/ simulation study given but not limited to,
-
- Initial laboratory Hypothesis:
-
- The final solution in the same vial.
-
- The final solution in the new vial.
-
- Re-dilution of stock solutions.
-
- Filter compatibility/ conditioning.
-
- Extra sonication.
-
- Any other’s.
-
- Extended Laboratory Hypothesis:
-
- Sonication temperature increase/ decrease/ too much chilled.
-
- Uses of wrong solvent/ reagents.
-
- Challenging of solution stability.
-
- Glassware contamination.
-
- Any other’s
Annexure – 5: Hypothesis/ Simulation study protocol
| Material Name | AR No. | ||
| Supplier/Mfg. | Batch No. | ||
| Mfg Date | Expiry Date |
- Purpose:- The purpose of this Protocol is to perform the Hypothesis/simulation study of the product/material to identify the root cause of failure.
- Scope: This protocol is applicable to the QC department of pharma company.
- OOS Details :
| Date of analysis | Name of analyst | Test | Results | Specification |
- Experimental Plan :
- Initial laboratory Hypothesis: ( e.g Final solution in the same vial. , Final solution in the new vial, Re-dilution of stock solutions, Filter compatibility/ conditioning, Extra sonication, Any other).
- Extended Laboratory Hypothesis: ( g Sonication temperature increase/ decrease/ too much chilled, Uses of wrong solvent/ reagents, Challenging of solution stability, Glassware contamination, Any other ).
- Justification for re-sampling (if any) [ based on hypothesis] :
- Sample Quantity :
- Final conclusion :
| Prepared By:
Date: |
Checked By:
Date: |
Approved By:
Date: |
(* Note: The experimental plan can be customized depending upon the type of failure to identify the root cause of OOS result )
Annexure – 6: Acceptance criteria for the replicate result.
| S.No. | Test parameters | Acceptance Criteria |
| 1 | Assay for Drug substances, in-process and chromatographic purity. | % RSD NMT 2.0 |
| 2 | Assay for Drug products. | % RSD NMT 2.0 (for drug content more than 0.5mg).
% RSD NMT 3.0 (for drug content less than or equal to 0.5mg). |
| 3 | Content of Preservative /Anti-Oxidant. | % RSD NMT 5.0. |
| 4 | Water content/LOD test:
a) When observed results ≤ 0.20%. b) When observed results ≥ 0.20% and ≤ 1.0%. c) When observed results ≥ 1.0% and ≤ 3.0%. d) When observed results ≥ 3.0%. |
a) Not Applicable
b) % RSD NMT 25%. c) % RSD NMT 15%. d) % RSD NMT 10%. |
| 5 | Residual solvents:
a) When observed results ≥ 100 ppm. b) When observed results ≤ 100 ppm and ≥ 50 ppm. c) When observed results ≤ 50 ppm and ≥ 10 ppm. d) When observed results ≤ 10 ppm. |
a) % RSD NMT 15%. b) % RSD NMT 25%. c) % RSD NMT 30%. d) Not Applicable. |
| 6 |
Related substance:a) When observed results ≤ 0.05%. b) When observed results ≥ 0.10% and ≤ 0.2%. c) When observed result ≥ 0.20% and ≤ 0.50% d) When observed results ≥ 0.50%. |
a) Not Applicable.
b) % RSD NMT 20%. c) % RSD NMT 15%. d) % RSD NMT 10%. |
| 7 | Specific gravity, specific optical rotation. | % RSD NMT 20.0. |
| 8 | Content uniformity/Dissolution/ Microbial assay | Meets the pharmacopeia requirements. |
| 9 | Residue on Ignition/Sulphated Ash. | The difference of the individual values shall not be more than ± 0.03. |
| 10 | Particle size by light diffraction measurement. | % RSD NMT 10% for any central value of the distribution (e.g. for x50) and %RSD NMT 15.0% for x10 and x 90.
Below 10 µm, these %RSD criteria shall be doubled. |
| 11 | Powder blend/mixture uniformity.
|
Meets the requirements as per validation protocol or SOP. |
| 12 | Note: In the case where any single known from LOQ to 0.1% / >0.1% accounts as a total impurity, the % RSD of total impurity shall be considered as NMT 20.0 and NMT 15.0 respectively. | |
Note: Follow the above-stated limits unless otherwise, these need to be changed based on the type of formulations and dosage form. While deciding these limits analytical method validation shall be referred.
Annexure – 7: Guidance for the handling of Human Error
| Error | Corrective Action | Preventive Action |
| Knowledge Based | Procedural requirements
Train Employee |
Review of Department Training Program
Close Gaps |
| Lapse Based | Counsel Employee (Verbal, Written, Disciplinary) | GMP training |
| Cognitive Based | Match Employee to Abilities | Evaluate Knowledge Assessment Effectiveness |
| Value Based | Counsel Employee (Verbal, Written, Disciplinary) | GMP training |
| Skill Based | Match Employee to Abilities | Evaluate Knowledge Assessment Effectiveness |
| Time Pressure | Assessment of resources
Reassign duties Create or Update Plans (Planning) |
Conduct process FMEA |
| Inadequate Equipment | Increase Inspection and Checks
Equipment Lock Out / Tag Out Re qualify / Revalidate after fixing or replacing Equipment |
Evaluate the adequacy of Qualification / Validation Resources and Procedures.
Close Gaps |
| Fatigue | Assessment of resources
Plant layout study Reassign Duties |
Flow chart Processing
Conduct Process FMEA Evaluate Resources Lading Close Gaps |
| Inexperience | Match Employee to Abilities | Evaluate Knowledge Assessment Effectiveness |
| Design and Construction Deficiencies | Increase Inspection and Checks
Equipment Lock Out / Tag Out Re qualify / Revalidate after fixing or replacing Equipment |
Evaluate the adequacy of Qualification / Validation Resources and Procedures.
Close Gaps |
| Unworkable Procedures | Revise Procedure
Conduct Training to the new revision |
Flow chart Processing
Conduct Process FMEA Update procedure Conduct Training |



Pingback: Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) - SOP & Guideline - CSTORE TRAINING
Pingback: oos log in - trustrose
Pingback: Quality Metrics - New FDA Guideline - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Reprocess Rework of API and Drug Product - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Out of Specification (OOS) in Packaging Material - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Reduce Testing Procedure for Raw Material (API) - Guidelines - SOPs
Pingback: Analytical Method Transfer (USP 1224) Guideline - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Environmental Monitoring : Microbiological Analysis :: Guidelines - SOPs
Pingback: Good Laboratory Practices (GLP) - SOP & Guideline - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: SOP for Out of Trend (OOT) Analytical Test Results - Pharma Beginners
Pingback: Media Fill Validation - SOP for Process Simulation - Pharma Beginners